Lung’s Volumes and Capacities
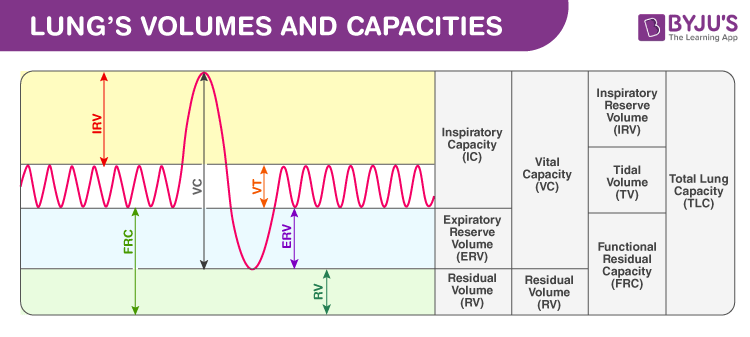
TV- The tidal volume is the total amount of air inhaled or exhaled during regular respiration or relaxed breathing. Approximately 500 ml of air is utilized during normal respiration in a healthy man.
IRV- An inspiratory reserve volume is a supplementary volume, approximately ranging between 2500 to 3100 ml of air which could be effectively inhaled after the inspiration of a standard tidal volume.
ERV- An expiratory reserve volume refers to the additional capacity of air which is about 1200 ml are that could be forcibly exhaled out after the expiration of a standard tidal volume.
RV- The residual volume is about the total volume of air around 1100 ml to 1200 ml residing in the lungs after the reserve volume is emitted or breathed out.
By adding up specific lung volumes we can find the values of lung capacities.
TLC- The total lung capacity applies to the total volume of air-filled in the lungs after a forced inspiration. The lung capacity of a healthy man is estimated to be 6000 ml.
TLC = TV + ERV + IRV + RV
VC – The vital capacity: is the total volume of air that can be expired after a maximum inhalation approximately 80 per cent TLC.
About 4800 ml approximately 80 per cent TLC.
VC = TV + ERV + IRV
IC- The inspiratory capacity is the total volume of air that can be inspired which is about 3600 ml.
IC = TV + IRV
FRC – The functional residual capacity is the total volume of air residing within the lungs after an exhalation process and it is about 2400 ml.
FRC = ERV + RV
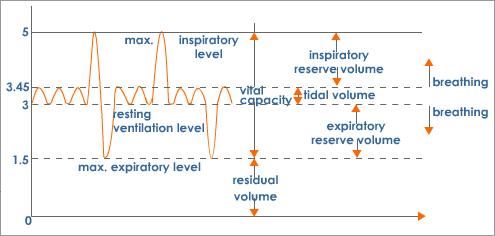
The residing air present within the lungs which does not participate in gas exchange is located in the portion of the airways inside the bronchi and bronchioles and outside the alveoli.
Comments
Post a Comment